What is
Sound?
Learning
Objectives
By the end of this unit, you will be able to
demonstrate an understanding of sound and vibrations by explaining the
following concepts: the nature of sound waves, the role of vibrations in
creating sound, the relationship between vibrations and the volume of sound,
the concept of pitch and its connection to vibration speed and frequency, the
importance of a medium for sound travel, and the measurement of sound using
decibels.
Understanding Sound and Vibrations
A sound
is a form of energy that travels in waves. These waves are caused by something
vibrating or moving rapidly back and forth. These vibrations can travel through the air and into your ear. When the
vibrating air reaches your eardrum, it also causes it to vibrate, enabling us
to hear the sound. The strength of these vibrations determines how loud or
quiet a sound is. Strong vibrations create loud sounds, while gentle vibrations
make quieter sounds.
Music, alarms, sirens, and speakers—sound is
all around us. But what exactly is sound, and how do we hear it? In this
episode of DEmystified, dive into a world of good vibrations as we explore the
science of sound. Click the image to watch the episode.
What are Sound Waves?
Sound
waves
are the invisible movement of sound energy that travels away from the source of
the sound. The farther these sound waves travel, the quieter the sound becomes.
Objects that produce sounds can create both high and low sounds.
Explore how sound travels through different
materials by clicking here.
The video below highlights the major
characteristics of sound waves and explains the significance of loudness,
compression, rarefaction, frequency, and pitch. The segment also discusses the
Doppler effect and provides a video quiz based on the segment's content.
The Pitch of Sound
A pitch
is a measure of how high or low a sound is. The pitch of a sound depends on the
speed of the vibrations that are creating it. Fast-moving vibrations create
high sounds, while slower-moving vibrations create low sounds. Frequency, which refers to the number
of vibrations in a certain time frame, also determines the pitch of a sound.
When you play a musical instrument with
strings, the length of the string can change the pitch. Shorter strings create
higher sounds, while longer strings produce lower sounds.
Click on the image to complete the “Study Jams” on Sound.
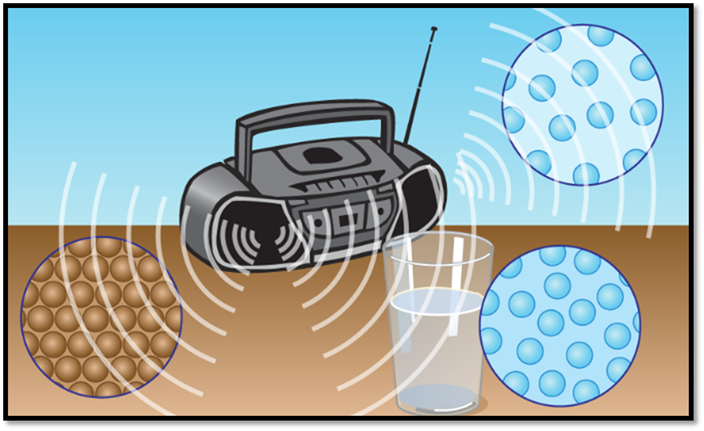
The Role of a Medium in Sound Travel
For sound to travel, it needs a medium, which can be a solid, a liquid,
or a gas. These mediums are made up of particles, and it is through these
particles that sound waves move. In other words, when an object vibrates, it
creates waves of energy that move through the medium, bouncing from particle to
particle until they reach your ear.
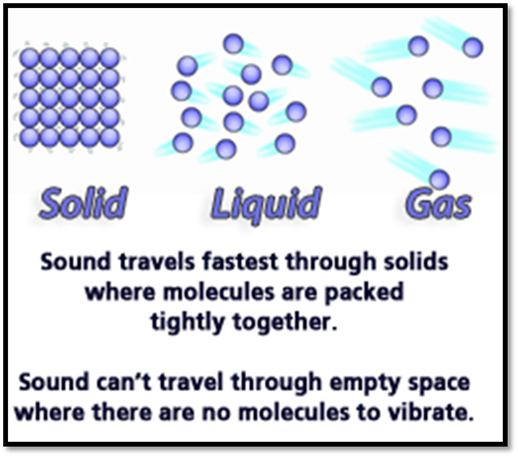
Sound waves spread out in all directions,
traveling fastest through solids because the particles in solids are very close
together. Sound waves travel slower through the air than solids or liquids
because air comprises gases. The particles that makeup gases are very far
apart, so it takes longer for the sound energy to move from one particle to
another in a gas.
New Path Learning
Interestingly, the temperature can also affect
the speed of sound. Sound travels faster through warm air than it does through
cooler air.
Watch the video below that explains how a
sound's medium and temperature can affect it.
Measuring Sound
Sound can be measured in units called decibels.
Click here to watch a video that provides examples of units used
to measure sound.
This measurement helps us understand the
intensity or loudness of a sound. So next time you "turn up the
volume," you're increasing the decibel level of the sound you're listening
to!

New Path Learning
A World of
Sounds
In conclusion, the world of sounds is a
fascinating array of loud to soft, high to low, and appealing to unappealing - all
made possible by vibrating particles journeying through various mediums. By
understanding sound scientifically, you can further appreciate the symphony of
sounds that fill our lives.
Click here for an interactive by New Path Learning.